
Second-line therapies include topical/intralesional/intravenous cidofovir, topical 5-fluorouracil, and topical ingenol mebutate. Patients who do not respond to first-line treatments may respond to other therapies or a combination of treatment modalities. Clinician-administered therapies include podophyllin, cryotherapy, bichloroacetic or trichloroacetic acid, oral cimetidine, surgical excision, electrocautery, and carbon dioxide laser therapy. Patient-administered therapies include podofilox (0.5%) solution or gel, imiquimod 3.75 or 5% cream, and sinecatechins (polypheron E) 15% ointment. Active treatment is preferable to watchful observation to speed up clearance of the lesions and to assuage fears of transmission and autoinoculation. Approximately one-third of penile warts regress without treatment and the average duration prior to resolution is approximately 9 months.
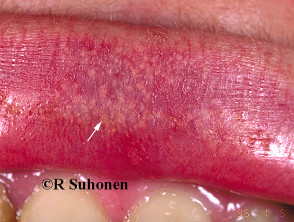
Lesions may be filiform, exophytic, papillomatous, verrucous, hyperkeratotic, cerebriform, fungating, or cauliflower-like.

Penile warts typically present as asymptomatic papules or plaques. Penile warts are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), notably HPV-6 and HPV-11.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
